The gene YLR012C is found on chromosome 7 near SSK1 in Saccharomyces cerevisae. It encodes a protein whose molecular functions, biological processes, and cellular components are unknown (SGD, 2004). YLR012C null mutants are viable, with no growth defects detected after 20 generations on YPD, as seen in figure 6. It does not appear to be an essential gene. A BLASTp search for YLR012C's amino acid sequence yielded only one hit other than the unknown Saccharomyces cerevisae protein itself; this protein is an unknown protein from Eremothecium gossypii, another species of yeast (NCBI, 2004). The BLASTp search also failed to reveal any conserved domains, so as of now this protein is a complete mystery.
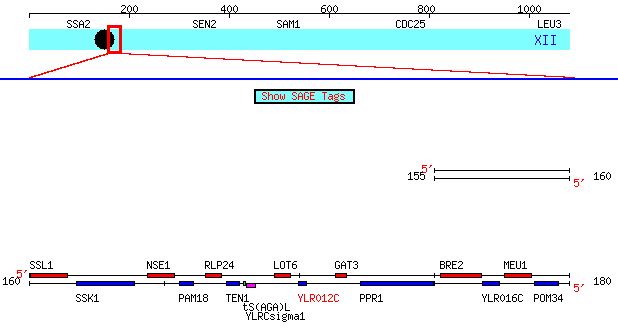
Figure 5: Chromosomal location of YLR012C. This diagram shows a region of Saccharomyces cerevisae chromosome 7 from the 159981 to the 180280 bp. The gene YLR012C is highlighted in red (SGD, 2004).

Figure 6:
Fitness score for YLR012C vs. the probability of its being essential. After growth on YPD for 20 generations, yeast cells with non-functional YLR012C experience no growth defects, indicating that YLR012C is not an essential gene (SGD, 2004).

Figure 7: BLASTp results from YLR012C. The only other hit is the protein AGR353Cp, located on chromosome 7 in Eremothecium gossypii (NCBI, 2004).