The Journal of Biological Chemistry Vol. 269,
No. 11, Issue of March 18, pp. 8255-8259, 1994
© 1994 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular
Biology, Inc.
From the +Department of Biology, The Johns
Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland 21218
and §The Biotechnology Center, The Ohio State University,
Columbus, Ohio 43210
¶ To whom correspondence should be addressed. Tel.: 410-516-5174;
Fax: 410-516-5213.
(Received for publication, September 3, 1993, and in revised form, November 22, 1993)
Chimeric cDNAs encoding a sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum
Ca ATPase (SERCA1) and regions of the Na,K-ATPase a-subunit
were constructed to seek the minimal region of the a-subunit
sufficient for assembly with the Na,K-ATPase ß-subunit.
cDNAs encoding a chimera and the chicken ß-subunit were
coexpressed in mammalian cells and assembly was assayed by immune
precipitation of the chimeric subunit with a monoclonal antibody
to the chicken ß-subunit. A chimera containing 26 amino
acyl residues of the Na,K-ATPase a1-subunit
(NDVEDSYGQQWTFEQRKIVEFTCHTA) (Asn894
to Ala919) that replaced the
corresponding avian SERCA1 Ca ATPase amino acyl residues (Thr871 to Thr898)
was able to assemble with the chicken ß-subunit. This a-subunit region is predicted to be extracellular,
located between membrane spanning domains 7 and 8 (H7-H8). Chimeras
that assembled with full length ß-subunit also assembled
with a ß-subunit chimera that retained only the ectodomain
of the chicken ß1-subunit. These results suggest that the
Na,K-ATPase a-subunit has the same
topology in the membrane as the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase,
probably with 10 membrane spanning domains, and that the aminoacyl
residues between membrane domains H7 and H8 are involved in assembly
with the ß-subunit in the extracellular/lumenal space.
Identification of domains involved in assembly of multisubunit membrane proteins can lead to an understanding of the mechanisms controlling assembly and may provide information about three dimensional structure. Expression of chimeric subunits and/or subunits lacking portions of their polypeptide chains has been a successful approach in identifying domains involved in subunit assembly (1-4).
The Na,K-ATPase is a heterodimer comprised of an ~100-kD a-subunit and a ~40-60-kDa glycoprotein ß-subunit. Both subunits are required for ion transport (5, 6). The a-subunit bears the ATP and cation binding sites and is therefore considered the catalytic subunit. The ß-subunit appears to be involved in the structural and functional maturation of the holoenzyme (7, 8) and subsequently transport to the plasma membrane (5, 9, 10). Assembly occurs during or soon after biosynthesis (11) and is required for exit from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)1 (12). In our continuing study of Na,K-ATPase subunit assembly, we have measured the ability of Na,KATPase ß-subunits to assemble with chimeras between the sarcoplasmic/ endoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase and the Na,KATPase a-subunits.
The sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPases are P-type
ATPases of ~100 kDa that lack a ß-like subunit. Some regions
of the Na,K-ATPase and Ca-ATPase show a high level of amino acid
sequence similarity, and hydrophobicity plots suggest that they
have similar topology in the membrane (13). Our earlier work with
the Na,K-ATPase/Ca-ATPase chimeras added further support to the
view that the two catalytic subunits have the same topology in
the membrane (1). Despite their similarities, the Ca-ATPase and
the Na,K-ATPase a-subunit have little
amino acid sequence similarity in the carboxyl-terminal third,
the region that contains the specific Na,K-ATPase a-subunit
aminoacyl residues necessary for assembly with the , ß-subunit.
Therefore, in making chimeras to define the assembly region more
closely, we could rely only on the patterns of hydrophobicity.
Using this guide, we constructed chimeric cDNAs encoding the Ca-ATPase
substituted by portions of Na,K-ATPase a-subunit
in the carboxyl-terminal region. Expression of these chimeric
cDNAs together with chicken Na,K-ATPase ß-subunit cDNA in
HeLa cells followed by precipitation of chimera-ß complexes
with a monoclonal antibody to the chicken ß-subunit allowed
us to seek the minimal Na,K-ATPase
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
cDNAs Used for Transfection - DNAs encoding the
The CC[c/n] cDNA, described earlier (1), was modified in this study to extend the sequence encoding Ca-ATPase by 48 nucleotides (16 amino acids). The other chimeras used in this study consisted of the chicken SERCA1 Ca-ATPase with short segments replaced by corresponding regions of the Na,KATPase. The Na,K-ATPase component and flanking SERCA1 aminoacyl sequences of these chimeras are shown in Fig. 4.
Cell Culture and Transfections - HeLa cells were grown in 35-mm tissue culture dishes in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium containing 5% fetal calf serum and 250 µg/ml gentamicin (medium, serum, and gentamicin from Life Technologies, Inc.). Transient expression was based on the recombinant vaccinia virus system (18) with the modifications as described earlier (1), except that 10 µg (10 µl) LipofectACETM cationic liposomes (Life Technologies, Inc.) were used for transfection experiments. Transfection efficiencies and relative levels of expression of transiently expressed proteins were determined as before (1).
Monoclonal Antibodies - Two monoclonal antibodies were used. Chicken specific monoclonal antibody CaF1-5C3-IgG (mAb-5C3) recognizes a cytosolic epitope of the Ca-ATPase (19). Chicken-specific monoclonal antibody ß24 (mAb-ß24) recognizes an epitope in the extracellular domain of the ß1-subunit (11, 20). These antibodies and the hybridomas that secrete them are available from the Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank, Department of Pharmacology, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD.
Metabolic Labeling and Immune Precipitation - Cells were labeled in methionine-free Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (Life Technologies, Inc.) containing 100-150 µCi/ml [35S]methionine and [35S]cysteine (Tran 35S-label; ICN Pharmaceuticals) for 3 h beginning 2 h or more after transfection. Detergent extracts were prepared from these cells, and immune precipitations were performed as described in Ref. 1 except that cell were solubilized with 75 µg/ml C12E8 detergent (Calbiochem) in buffer (10 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl), and antigen bound to immunobeads was washed four times with the same detergent buffer. mAb-ß24 was coupled to activated beads (oxidized cross-linked Sepharose CL-6B) by reductive amination reactions (21) as described earlier (1).
RESULTS
Assembly of Chimeric Proteins with Chicken ß-subunit
- We have shown that the carboxyl-terminal 161 amino acids of
the Na,K-ATPase a-subunit are sufficient
for assembly with the ß-subunit (1). In that study we used
mAb- ß24 that recognizes an epitope in the extracellular
domain of the ß-subunit that is exposed in native Na,K-ATPase.
The immune precipitation of
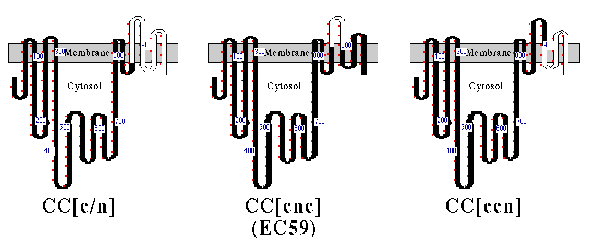
The structures of CC[c/n] (161 amino acids of the a-subunit), CC[c/n/c] (59 amino acids of the a-subunit), and CC[c/c/n] (103 amino acids of the a-subunit) chimeric proteins are depicted in Fig. 1, with their predicted topology in cell membranes. Each chimera or wild-type Ca-ATPase was coexpressed in HeLa cells with the chicken ß1 subunit, and assays for subunit assembly were performed (Fig. 2). As expected, CC[c/n] chimera assembled with the chicken ß-subunit (Fig. 2, lane 2), whereas the CC[c/c/n] chimera (Fig. 2, lane 4 ) and wild-type Ca ATPase (CCC; Fig 2, lane 5) did not. However, CC[c/n/c] (Fig. 2, lane 3), containing the proposed 59 amino acid H7-H8 domain of the a-subunit, did coprecipitate with the chicken ß-subunit, although the yield was much less than for the CC[c/n] chimera. This indicated that the 59 aminoacyl residues of the Na,KATPase a-subunit in chimera CC[c/n/c] were sufficient for assembly with the ß-subunit.

FIG. 1. Structure and predicted topology of chimeric proteins. A cartoon representation of CC[c/n], CC[c/n/c] (also referred to as EC59), and CC[c/c/n] are shown. Nomenclature for these constructs is set by three uppercase letters which represent amino-terminal, central, and carboxyl-terminal domains of the Na,KATPase (N) and Ca2+-ATPase (C) proteins. Bracketed lowercase letters replace an uppercase letter when junctions between the Na,K-ATPase or Ca2+-ATPase occur within the carboxyl-terminal domain. All the constructs are fit to the topology model proposed for the Ca2+ -ATPase (26). Portions of the chimeric protein representing Ca2+-ATPase (black) and Na,K-ATPase (white) are shown. Small red dots outside rectangles mark every 10 th residue, and numbers identify locations of residues bearing those position numbers. Amino acid numbering within the carboxyl terminus does not refer to corresponding residue numbers of the actual chicken Na,K-ATPasea1-subunit or the Ca2+-ATPase. This occurs because the two catalytic proteins differ slightly in their length. Residues within transmembrane domains were fitted from hydrophobicity plots and are considered approximate.
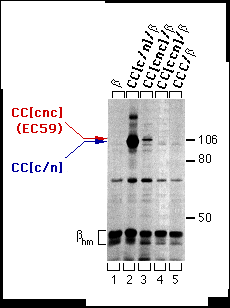
FIG. 2. Assembly of the CC[c/n] and CC[c/n/c] (also referred to as EC59) chimeras with the chicken ß-subunit in HeLa cells. Cells were infected with vaccinia virus then transfected with cDNAs encoding the ß-subunit alone or together with CC[c/n], CC[c/n/c], CC[c/ c/n], or CCC. Three hours post-infection, cells were metabolically labeled and extracts were prepared from these cells as described under "Experimental Procedures." Extracts were incubated with mAb-ß24 immunobeads, and the immune precipitations were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and fluorography. Positions of the molecular weight markers are indicated at the right. Positions of the CC[c/n]) and CC[c/n/c] chimeras are indicated at the left in the order of molecular mobility by SDS-PAGE from slower (red) to faster (blue). The protein bands representing the high-mannose forms of the ß-subunit (ßhm) are also indicated. Endogenous a-subunit, which assembles with the chicken ß-subunit at a much lower level, is barely detectable and thus not indicated.
To verify expression and to identify the apparent molecular weight of each of the chimeras (defined by electrophoretic mobility), we recovered chimeras and CCC by immune precipitation from supernatants that had previously been incubated with mAb-ß24 immunobeads. The mAb-5C3 (chicken-specific anti-Ca-ATPase antibody) immunobeads precipitated CC[c/n], CC[c/n/c], CC[c/c/ n], and CCC (Fig. 3, lanes 2-5). Therefore, CC[c/c/n] (Fig. 2, lane 4 ) was available for interactions with the ß subunit but did not assemble.

FIG. 3. Immune precipitations of CC[c/n], CC[c/n/c] (EC59), CC[c/c/n], and CCC proteins expressed in HeLa cells. Cells were infected with vaccinia virus then transfected with cDNAs encoding the ß subunit alone or together with CC[c/n], CC[c/n/c], CC[c/c/n], and CCC. Three hours post-infection, cells were metabolically labeled, and extracts were prepared from these cells as described under " Experimental Procedures." Extracts were first incubated with mAb-ß24 immunobeads followed by a second incubation with mAb-5C3 immunobeads, and the second immune precipitates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and fluorography. Positions of the molecular weight markers are indicated at the right. Positions of each of the chimeras are indicated at the left in the order of molecular mobility by SDS-PAGE from slowest (top) to fastest (bottom). Note that the cell extracts used here are the same extracts used in Fig. 2.
Because the yield of CC[c/n/c], from here on referred to as chimera EC59, coprecipitating with the ß-subunit was much less than for the CC[c/n] chimera, we wondered whether replacing the predicted extracellular H9 H10 domain of the Ca-ATPase with the corresponding a-subunit domain might increase the stability of the chimeras complex. EC5911, a chimera with the predicted extracellular H7-H8 domain (59 residues) and H9-H10 domain (11 residues) of the Na,KATPase a-subunit (Fig. 4), did coprecipitate with greater yield than the EC59 chimera (Fig. 5, lane 4). This suggests that although a- ß assembly interactions predominantly occur with the single Na,K-ATPase H7-H8 domain (EC59), the regions that associate during the assembly with the ß-subunit possibly include both the H7-H8 and H9-H10 domains (EC5911).
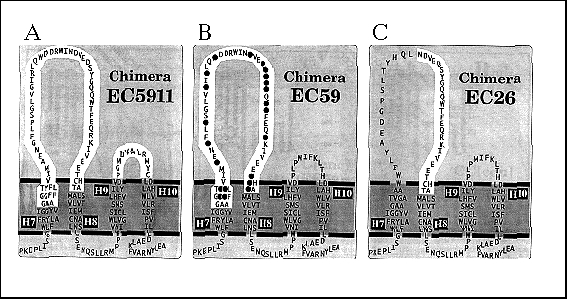
FIG. 4. Cartoon representation of carboxyl terminus of EC5911, EC59, and EC26 chimera H7-H8 domains depicted in the membrane. EC5911 chimera is predicted to have Na,K-ATPase a-subunit residues (highlighted ) in both the extracellular H7-H8 domain and H9-H10 domain. EC59 and EC26 chimera have Na,K-ATPase a-subunit residues (highlighted ) only in the predicted H7-H8 extracellular domain. EC59 shows black circles over amino acid residues found to be identical in both Na,K-ATPase and H,K-ATPase a-subunit sequences. Residues within transmembrane domains were fitted from hydrophobicity plots and are considered approximate. Ca2+ -ATPase residues are shown outside highlighted areas. Not shown are the Ca2+ ATPase residues 1- 823 that comprise that rest of each chimera.
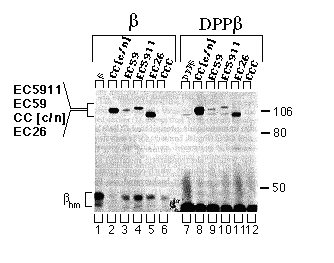
FIG. 5. Assembly of the CC[c/n], EC59, EC5911, and EC26 chimeras with the chicken ß-subunit or the DPPß-subunit chimera in HeLa cells. Cells were infected with vaccinia virus then transfected with cDNAs encoding the ß-subunit or DPPß-subunit chimera alone or together with CC[c/n], EC59, EC5911, EC26, or CCC. Three hours post infection, cells were metabolically labeled, and extracts were prepared from these cells as described under "Experimental Procedures." Extracts were incubated with mAb- ß24 immunobeads, and the immune precipitations were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and fluorography. Positions of the molecular weight markers are indicated at the right. Positions of the CC[c/n], EC59, EC5911, and EC26 chimeras are indicated at the left in the order of molecular mobility by SDS-PAGE from slowest (top) to fastest (bottom). The protein bands representing the high-mannose forms of the ß-subunit and DPPß-subunit chimera (ßhm) are also indicated. Endogenous a-subunit, which assembles with the chicken ß subunit at a much lower level and has approximately the same molecular mobility as the EC26 chimera, is detectable in the DPPß-subunit samples but not in the ß-subunits samples.
Sequence alignments of the amino acid acyl residues in the
proposed H7 H8 domain of the a-subunit
revealed a cluster of residues well conserved among all the known
Assembly of Chimeric Proteins with the Extracellular Domain of Chicken ß-subunit - HeLa cells coexpressing chimeric catalytic subunits and a chimeric DPPß-subunit protein, retaining only the extracellular domain of the chicken ß1-subunit, were assayed for subunit assembly as described above. CC[c/n], EC59, EC5911, and EC26 (Fig. 5, lanes 8-11 ) assembled with the chimeric DPPß-subunit, although the yield of each of the chimeric proteins appeared to be less than the yield when the wild-type ß1-subunit was used. The CCC catalytic subunit did not assemble with the wild-type ß-subunit and also failed to assemble with the chimeric DPPß-subunit (Fig. 5, lane 12).
To verify expression and to identify the characteristic apparent molecular weight of each of the chimeras, we recovered chimeras and CCC by immune precipitation from supernatants that had previously been incubated with mAb- ß24 immunobeads. As expected, mAb-5C3 (chicken specific anti-Ca-ATPase antibody) immunobeads precipitated CC[c/n], EC59, EC5911, EC26, and CCC (Fig. 6, lanes 2 - 6). It was important to verify the presence of the EC26 chimera, since it has an apparent molecular weight (electrophoretic mobility) similar to that of the endogenous a-subunit, which coprecipitates with low yield (for endogenous a-subunit background see Fig. 5, DPPß set, lanes 7 - 12).
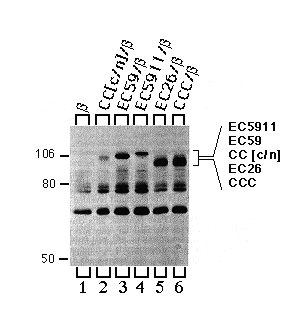
FIG. 6. Immune precipitations of CC[c/n], EC59, EC5911, EC26 and CCC proteins expressed in HeLa cells. Cells were infected with vaccinia virus, then transfected with cDNAs encoding the ß-subunit alone or together with CC[c/n], EC59, EC5911, EC26, and CCC. Three hours post infection, cells were metabolically labeled, and extracts were prepared from these cells as described under "Experimental Procedures." Extracts were first incubated with mAb-ß24 beads followed by a second incubation with mAb-5C3 immunobeads, and the second immune precipitates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and fluorography. Positions of the molecular weight markers are indicated at the left. Positions of each of the chimeras are indicated at the right in the order of molecular mobility by SDS-PAGE from slowest (top) to fastest (bottom). Note that the cell extracts used here were the same extracts that had previously been used for the experiments illustrated in Fig. 5.
DISCUSSION
Transfection efficiencies and levels of expression were approximately
equivalent throughout our experiments, and therefore the yields
of different chimeras in the assembly assay should reflect relative
efficiencies of assembly or relative stabilities of the assembled
Our results demonstrate that an extracellular domain consisting of 26 amino acyl residues (NDVEDSYGQQWTFEQRKIVEFTCHTA) of the Na,KATPase a-subunit is sufficient for assembly with the Na,KATPase ß subunit when these 26 residues lie in the H7-H8 lumenal loop of the SERCA1 Ca-ATPase. Furthermore, this chimera will assemble with a chimera that contains only the ectodomain of the Na,K-ATPase ß-subunit (15). The assembled forms assayed in this study may represent intermediate states in the assembly-maturation process rather than mature functional forms. Since we know that subunit assembly occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum, we can conclude that the interactions involved in assembly of the a- and ß-subunits of the Na,K-ATPase must occur largely in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. Subunit assembly involving extracellular domains has been observed with a few other oligomeric plasma membrane proteins (see review Ref. 22).
Two independent studies have defined epitopes between the predicted seventh and eighth membrane-spanning domains of the Ca-ATPase that are exposed to the lumen of the sarcoplasmic reticulum (23, 24), and these results were interpreted to support a 10 membrane-spanning domain model of the calcium pump (25, 26). It is this epitope region in the chicken SERCA1 that we have replaced with 26 aminoacyl residues of the Na,KATPase. Since the resulting chimera, EC26, assembled with the ß subunit, one can infer that at least up to membrane span H8, the COOH-terminal end topologies of the Ca-ATPase and Na,K-ATPase a-subunit are the same.
Identification of an extracellular region between the seventh and eighth membrane spans of the gastric H,K-ATPase a-subunit has been presented (31). This region is homologous to the region of the Na,K ATPase a-subunit our report identifies as part of the subunit assembly site. The Na,K-ATPase and H,K-ATPase a-subunits share ~62% amino acid sequence identity (32), and each associates with a ß-like subunit. Sequence alignment of amino acids in the predicted H7-H8 domain of Na,KATPase and H,K-ATPase a-subunits reveals clusters of amino acids closest to the H8 domain that are identical throughout all species. Chimera EC26 contained these conserved aminoacyl residues.
The Na,K-ATPase a-subunit has been predicted to have from three to six membrane-spanning domains in its carboxyl-terminal ~300 amino acids (13, 27-29). These predictions were based upon hydrophobicity analysis and results of immunological and proteolysis studies. Recently Maguire and colleagues (30) showed more conclusively that a prokaryotic P-type Mg-ATPase has 10 membrane-spanning domains. In our experiments, EC5911, containing the predicted H7-H8 and H9-H10 extracellular domains, consistently appeared to assemble better with the ß-subunit than did EC59. This suggests that subunit interactions stabilizing the assembled state may also involve the a-subunit's hypothetical H9-H10 domain. Complicating this interpretation is the fact that both EC59 and EC5911 appeared to assembly more poorly than EC26. Chimeras EC59 or EC5911 contain aminoacyl residues of the Na,KATPase a-subunit predicted to be part of the membrane-spanning H7 domain. Perhaps these residues partially disturb the optimal structure at the H7-H8 domain, distorting the presentation of the a-subunit assembly residues to the ß-subunit.
It is difficult to speculate about what types of molecular interactions might be most important between the a- and ß-subunits. Studies with the multisubunit ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase have identified various types of interactions at the interfaces between assembled subunits (33). Flachmann et al. (33) found that replacement of a single critical aminoacyl residue completely abolished assembly. Amino acids substitutions in the Na,K-ATPase a-subunit assembly domain may also allow us to identify a few of the critical amino acids.
Acknowledgments - We thank Dr. Carolyn Machamer and Dr. Ora Weisz (The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD) for help with the vaccinia virus/T7 expression system, Delores Somerville and Christine Hatem for technical assistance, and Yuanyi Feng and Mitch Kostich for suggestions during the writing of the manuscript.
* This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants GM44373 (to K. T.) and NS-23241 and HL-27867 (to D. M. F.) The costs of publication of this article were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. This article must therefore be hereby marked "advertisement" in accordance with 18 U.S.C. Section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.
Footnote
1. The abbreviations used are: ER, endoplasmic reticulum; SERCA,
sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase; C12E8, octaethyleneglycol dodecyl ether; PAGE, polyacrylamide
gel electrophoresis; mAb, monoclonal antibody.
REFERENCES
1. Lemas, M. V., Takeyasu, K., and Fambrough, D. M. ( 1992)
J. Biol. Chem. 267, 20987-20991
2. Lippincott-Schwartz, J., Bonifacino, J. S., Yuan, L., and Klausner,
R. D. (1988) Cell 54, 209-229
3. Yu, X.-M., and Hall, Z. W. (1991) Nature 352,
64 67
4. Verrall, S., and Hall, Z. W. (1992) Cell 168,
23-32
5. Noguchi, S., Mishina, M., Kawamura, M., and Numa, S. (1987)
FEBS Lett. 225, 27-32
6. Horowitz, B., Eakle, K. A., Scheiner-Bobis, G., Randolph, G.
R., Chen, C. Y. Hitzeman, R. A., and Farley, R. A. (1990) J.
Biol. Chem. 265, 4189-4192
7. Ackermann, U., and Geering, K. (1990) FEBS Lett. 269,
105-108
8. Geering, K., Theulaz, 1., Verrey, F., Hauptle, M. T., and Rossier,
B. C. (1989) Am. J. Physiol. 257, C851-C858
9. Fambrough, D. M. (1988) Trends Neurosci. 11,
325-329
10. Takeyasu, K., Renaud, K. J., Taormino, J., Wolitzky, B. A.,
Barnstein, A., Tamkum, M. M., and Fambrough, D. M. (1989) Curr.
Top. Membr. Transp. 34, 143-165
11. Fambrough, D. M., and Bayne, E. K. (1983) J. Biol. Chem.
258, 3926-3935
12. Jaunin, R. Horisberger, J. D., Richter, K., Good, P. J., Rossier,
B. C., and Geenng, K. (1992) J Biol. Chem. 267,
577-585
13. Takeyasu, K., Lemas, V, and Fambrough, D. M. (1990) Am.
J. Physiol. 259, C619-C630
14. Renaud, K. J., Inman, E. M., and Fambrough, D. M. ( 1991)
J. Biol. Chem. 266, 20491-20497
15. Hamrick, M., Renaud, K. J., and Fambrough, D. M. ( 1993) J.
Biol. Chem. 268, 24367-24373
16. Takeyasu, K., Tamkun, M. M., Renaud, K. J., and Fambrough,
D. M. ( 1988) J. Biol. Chem. 263, 4347-4354
17. Karin, N. J., Kapnelian, Z., and Fambrough, D. M. (1989) Mol.
Cell. Biol. 9, 1978-1986
18. Fuerst, T. R., Earl, P. L., and Moss, B. (1987) Mol. Cell.
Biol. 7, 2538-2544
19. Kapnelian, Z., and Fambrough, D. M. (1987) Dev Biol. 124,
490-503
20. Tamkun, M. M., and Fambrough, D. M. (1986) J. Biol. Chem.
261, 1009-1019
21. Stults, N. L., Asta, L. M., and Lee, Y. C. ( 1989) Anal.
Biochem. 180, 114-119
22. Hall, Z. W. (1992) Trends Cell Biol. 2, 66-68
23. Clarke, D. M., Loo, T. W. and MacLennan, D. H. (1990) J.
Biol. Chem. 265, 17405-17408
24. Matthews, 1., Sharma, R. R. Lee, A. G., and East, M. M. (1990)
J Biol. Chem. 265, 18737-18740
25. MacLennan, D. H., Brandl, C. J., Korezak, B., and Green, N.
M. (1985) Nature 316, 696-700
26. Brandl, C. J., Green, N. M., Korezak, B., and MacLennan, D.
H. (1986) Cell 44, 597-607
27. Shull, G. E., Schwartz, A., and Lingrel, J. B. (1985) Nature
316, 691-695
28. Ovchinnikov, U. A., Modyanov, N. N., Broude, N. E., Petrakhin,
K. E., Grishin, A. V., Arzamazova, N. M., Aldanova, N. A., Monastyrskaya,
G. S., and Sverdlov, E. D. (1986) FEBS Lett. 201,
237-245
29. Capasso, J. M., Honng, S., Tal, D. M., Goldshleger, R., and
Karlish, S. J. D. ( 1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267, 1150-1158
30. Smith, D. L., Tao, T., and Maguire, M. E. (1993) J.
Biol. Chem. 268, 22469-22479
31. Bamberg, K., Mercier, F. Reuben, M. A., Kobayashi, Y., Munson,
K. B., and Sachs, G. (1992) Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1131,
69-77
32. Shull, G. E., and Lingrel, J. B. (1986) J. Biol.
Chem. 261, 16788-16791
33. Flachmann, R., and Bohnert, H. J. (1992) J. Biol. Chem.
267,10576-10582.
©
Copyright 2000 Department of Biology, Davidson College, Davidson,
NC 28036
Send comments, questions, and suggestions to: macampbell@davidson.edu