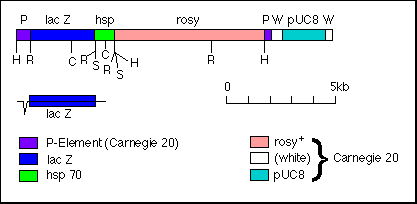
The purpose of plasmid rescue is to isolate the chromosomal DNA adjacent to an inserted piece of DNA. There are 4 steps to this process.
1) At the beginning, a piece of DNA has inserted into the chromosome: (see original paper)

2) Isolate the genomic DNA (gDNA) and digest it with a restriction enzyme that will cut at the edge of the plasmis protion of the insert. In this example, you would use Hind III.

3) Clean and concentrate the DNA, and do a ligation on the digested gDNA but do not add a plasmid.

4) Transfrom the ligation into E. coli and look for colonies. Any cells that survive antibiotic selection must have some flanking chromosomal DNA in the plasmid.
Return To Molecular Biology Main Page
©
Copyright 2000 Department of Biology, Davidson College, Davidson,
NC 28036
Send comments, questions, and suggestions to: macampbell@davidson.edu