 |
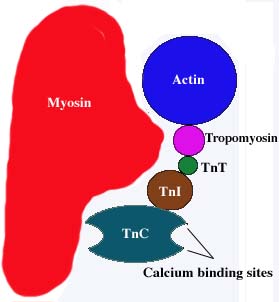
| Fig. 1. A cartoon of the Troponin complex within the muscle cell. Shown are the position of the Troponin proteins (T, I, C), in relation to actin, myosin and tropomysin. Adapted from Zot and Potter, 1987. |
Troponin C (TnC) is part of the troponin protein complex (comprised of Troponins C, I, and T) which helps position tropomysin along the thin filament in muscle cells (Campbell, 1996) via calcium-dependent regulation (Vassylyev et al., 1998). This troponin complex is found in all muscle cells, though there are different isoforms of the proteins between different types of muscle cells (e.g., cardiac and skeletal muscle cells, see Homo sapiens and Xenopus laevis sequences). Specifically, it is TnC that binds to 2 calcium cations, while TnI binds to actin, and TnT binds to tropomysin (Voet and Voet, 1995).
 |
| Fig. 1. A cartoon of the Troponin complex within the muscle cell. Shown are the position of the Troponin proteins (T, I, C), in relation to actin, myosin and tropomysin. Adapted from Zot and Potter, 1987. |
|
|
| Fig. 2. Chicken (Gallus gallus) TnC (MMDB Id: 5512 PDB Id: 1NCZ) |
|
|
|
|
| Caenorhabditis elegans |
|
|
| Drosophilia silvestris |
|
|
| Gallus gallus |
|
|
| Homo sapiens |
|
|
| Homo sapiens |
|
|
| Xenopus laevis |
|
|
| Xenopus laevis |
|
|
References:
Campbell NA. 1997. Biology, 4th ed. Menlo Park, CA: Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Company.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. 2000 March 9. NCBI Home Page. <http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov:80/>. Accessed 2000 March 19.
Vassylyev DG, Takeda S, Wakatsuki S, Maeda K, Maeda Y. 1998. Crystal structure of troponin C in complex with troponin I fragment at 2.3-A resolution. Proc. Nat. Sci. USA 95(9):4847-52.
Voet D, Voet JG. 1995. Biochemistry. New York, NY: J. Wiley and Sons, Inc.
Zot AS, Potter JD. 1987. Structural aspects of troponin-tropomyosin regulation of skeletal muscle contraction. Ann. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 16: 535-559.
Back to the Davidson College Molecular Biology Page
Back to Aaron Rice's Main Page
©2000 Department of Biology, Davidson College, Davidson, NC 28036
Comments? Questions? email: aarice@davidson.edu