Enhanced Chemiluminescence
(ECL) Detection of DNA or RNA
adapted from Amersham's protocol
Introduction
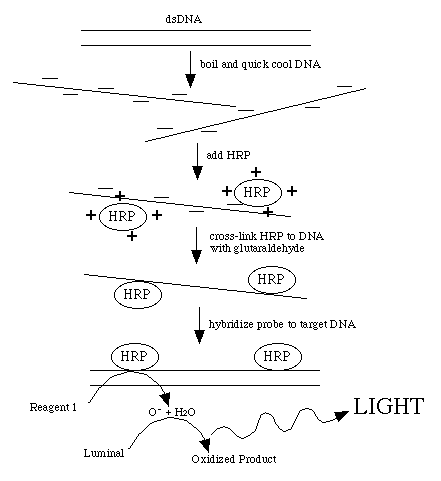
This procedure directly labels probe DNA or RNA with horseradish peroxidase
(HRP). This is achieved by completely denaturing the probe into a single-stranded
form. The peroxidase has been complexed with a positively charged polymer
which causes the HRP to form a loose attachment to the negatively charged
nucleic acid. This ionic interaction can be disrupted by counter ions so
the probe must be in a very low-salt solution. After the probe and HRP have
associated, glutaraldehyde creates covalent bonds between the HRP and the
probe.
Once the probe is labeled, it can be used immediately
to detect DNA or RNA bound to a membrane. From this stage on, it is important
to ensure that the enzyme activity is not lost, so do not expose the labeled
probe to high temperatures. Amersham has provided us with a optimized hybridization
buffer which ensures efficient hybridization while protecting the enzyme's
activity. The buffer includes 6M urea (equivalent to 50% formamide) which
reduces the melting temperature (Tm) of the hybridization. Therefore, when
controlling stringency of the hybridization, the only parameter which may
be altered is salt concentration.
After hybridization, the membranes are washed to
remove non-hybridized probe, again making sure not to inactivate the HRP.
Stringency of the washing conditions may be altered by adjusting the urea
or SSC concentration in the primary wash buffer. If an urea wash is not
used, the temperature of this wash can be raised to a maximum of 55 C, provided
the wash is performed for no longer than 2 X 10 minutes. The washed filters
can be taken directly to the ECL detection or stored moist in saran wrap
at 4° C.
Detection reagent #1 decays to H2O2 , the substrate for HRP. Reduction of H2O2 by the enzyme is coupled to the light producing reaction
by detection reagent #2. This contains luminol which produces a blue light
when oxidized. The light production is increased and prolonged by the presence
of an enhancer reagent in the detection solutions.
Labeling the Probe
This protocol is designed to label 100
ng of probe DNA of at least 250 bp in length. This may be scaled up to label
more probe when necessary (e.g. bigger blots, little target DNA, low percent
homology of probe to target, and reduced length of probe). Normally, using
10 ng of probe/ ml of hybridization solution is sufficient. The best probes
(high signal to noise ratio) are produced when the insert is isolated from
the plasmid DNA.
- Purify the DNA to be used as probe and dissolve
in either dH2O.
Quantify the amount of probe DNA by measuring the optical density
(OD) at 260 nm (OD260). To convert an OD to DNA concentration, use the following
conversion factors:
OD260 of 1 = 50 µg/ ml dsDNA
OD260
of 1 = 40 µg/ ml ssDNA
OD260of
1 = 30 µg/ ml ssDNA oligonucleotide
- Dilute 100 ng of DNA into a final volume of 10
µl of specially deionized water (supplied in kit).
- Denature DNA by heating in a boiling water bath
for 5 minutes. Immediately cool the DNA on ice for 5 minutes. Spin this
briefly (3 seconds) in a microfuge to collect all liquid at the bottom
of the tube.
- Add an equal volume (10 µl) of DNA labeling
reagent (supplied in kit) to the cooled DNA. Mix gently but thoroughly.
- Add the glutaraldehyde solution, using a volume
equivalent to the volume of labeling reagent (10 µl). Mix thoroughly.
If necessary, spin briefly in microfuge to collect contents at the bottom
of the tube.
- Incubate for 10 minutes at 37° C.
- If not used immediately, the probe can be stored
on ice for a short period (10 - 15 minutes). Labeled probes may be stored
in 50% glycerol at -20° C for up to 6
months with no further treatment of the probe.
Hybridization and Washing of Blot
- Prepare the hybridization buffer as follows:
- At room temperature, take the required volume
of hybridization buffer (generally, 250 µl/ cm2 of membrane for small blots).
- Add reagent grade solid NaCl to a final concentration
of 0.5 M (this is the variable to determine stringency).
- Add the blocking reagent (supplied in kit) to
a final concentration of 5% (w/v). Immediately mix thoroughly to get the
blocking reagent into a fine suspension. Continue mixing at RT° for one hour on a magnetic stirrer then heat to 42°
C for 30 - 60 minutes with occasional mixing. Excess
buffer can be aliquotted in sterile plastic container and stored at -20° C for at least 3 months.
- Place the blots in 42°
C hybridization buffer and prehybridize for 15- 60 minutes at 42° C with gentle agitation. Be sure and remove any bubbles
before sealing bag.
- Add labeled probe (10 ng/ml) to the pre-hybridization
buffer and mix gently before sealing the bag. Avoid placing the probe directly
on the membrane. Incubate overnight at 42°
C. When the copy number of the target DNA is high, this hybridization can
be reduced to 1 - 4 hours.
- Prepare the primary wash bufffer and preheat
to 50° C.
Next Day
- Wash 2 X 5 minutes and no longer than this!.
- Place the blots in a similar volume of secondary
wash solution and agitate for 2 X 5 minutes at RT°.
Do not allow the blot to dry.
Detection of Probe (in Dark Room)
- Cover the bench with a square piece of saran
wrap (roughly 1 sq. foot). Have a second piece (2 feet long)
ready that is not taped down.
- Mix equal volumes (3 ml each) of detection reagents
1 and 2 immediately before use. Mix them immediately before use since they
inactivate each other quickly.
- Drain excess secondary wash from blot and place
blot (DNA side up) on the saran. Pour the mixed detection reagents onto
the blot - do not let blot dry out!
- Incubate for exactly 1 minute at RT°. Drain off excess detection solutionon a old film that
is wrapped in saran with the DNA side UP. The blot is now emitting light
so we must work quickly.
- In the darkroom and under red lighting, expose
the X-ray film for 2 hours.
Developing X-ray film
- Put the film in the tray of developer but do
not scrape the film with the tongs. Process the film using these directions:
- Dilute 217 ml of developer up to 1 L with RT° water
- Dilute 217 ml of fixer up to 1 L with RT° water.
- Immerse the film smoothly into the developer
for a maximum of 5 minutes. However, watch the film as it develops. You
may stop it at any time.
- When it is time, immerse the film in water to
wash off the developer.
- Immerse the film in fixer for a 3 minutes. (At
this point, the film is white light safe.)
- Immerse the film in fresh water for 3 minutes
to wash off any water.
Solutions Required for ECL DNA
detection
primary wash buffer without urea
amount reagent = final concentration
- 700 ml water
- 20 ml 20% SDS = 0.4%
- 25 ml 20X SSC = 0.5X SSC (or use 5 ml for 0.1X
SSC; high stringency)
- after dissolved, bring final volume up to 1 L
secondary wash buffer
amount reagent final concentration
- 100 ml 20X SSC = 2X
- 900 ml water
20X SSC
- 175.3 g NaCl
- 88.2 g sodium citrate
- 800 ml water
- adjust pH to 7.0 with a few drops of 10M NaOH
- adjust volume to 1 L with water
Lab Schedule Outlined
Lab Schedule In Context of Research Project
Molecular Biology Main Page
Course Materials
Biology Main Page


© Copyright 2002 Department of Biology, Davidson College, Davidson, NC 28036
Send comments, questions, and suggestions to: macampbell@davidson.edu

