This web page was produced as
an assignment for an undergraduate course at Davidson College.
My Favorite Yeast ORFs: UBI4 and SET4
Using Microarrays to Look at
Gene Expression
This web page considers expression of the yeast genes UBI4 and SET4 using data from microarrays. Information on gene expression from microarrays, or DNA chips, is available from the following databases: Expression Connection, the Yeast Microarray Global Viewer (yMGV), the Stanford Microarray Database (SMD), and the Claude Jacq lab Microarray Page. Expression of annotated genes involved in known pathways can be seen using the application, GenMAPP.
UBI4 encodes ubiqutin, a protein found in the cytoplasm of S.cerevisiae involved in protein degradation tagging. UBI4 expression is associated with stress response.
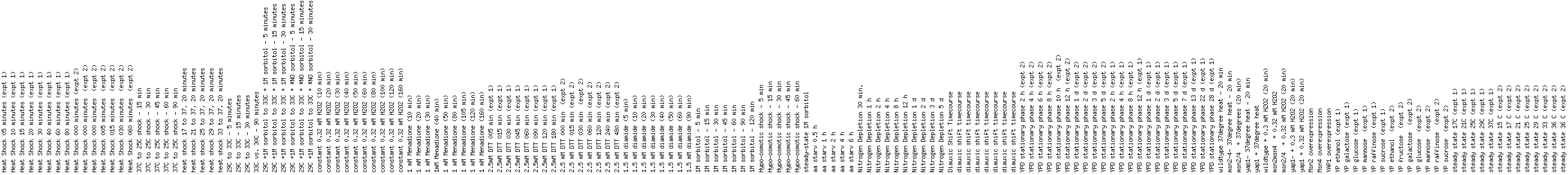
Scale : (fold repression/induction)
![]()
|
ORF |
Gene |
|
|
UBI4 |
||
|
GSP2 |
||
|
SSA4 |
||
|
GRE3 |
Figure 1: Microarray data for
UBI4 showing expression in response to stress.
Three similar genes are shown, with a Pearson correlation of > 0.8 to
UBI4. Click on a color strip to see
data for that gene. Courtesy of Expression
Connection.
According
to this data, UBI4 changes its expression over time under conditions of
stress. Expression changes are
noticeable for individual stress conditions over time. UBI4 expression patterns are specific. It will not be induced in response to any
stress, but rather will be induced in situations where the cell needs increased
amounts of ubiquitin to target proteins for degradation
SET4 is
a non-annotated ORF found on chromosome 10 of S.cerevisiae. Using
the program PREDATOR and Kyte-Doolittle analysis it was predicted that SET4
does not encode a transmembrane protein.
Predictions can be made about SET4’s function by looking at its
expression pattern.
A paper
by Linde, et al. shows that SET4 is induced under anaerobic
conditions. The cells used in this
study are described as follows: “The
cultures (strain CEN.PK113-7D (MATa))were fed with a defined mineral medium
containing glucose in an Applikon laboratory fermentor. The dilution rate was
0.1h-1 at 30°C, pH was 5.0. Aerobic conditions were maintained by sparging the
cultures with air (0.5 liter.min-1). For anaerobic cultures, the medium was
supplemented with Tween 80 and ergosterol. Anaerobic conditions were maintained
by sparging the medium with pure nitrogen gas (0.5 liter.min-1).” yMGV,
2001

Figure 2:
This chart shows SET4 induction (red) on a log2 scale for five trials under
conditions of anaerbic respiration. The thin red and green lines designate one
fold induction and repression.
Experiments were performed by the Linde lab. Courtesy of yMGV.
Only
383 (6.2%) of the 6169 ORFs tested showed 2 fold induction under anaerobic
conditions. SET4 is part of the
6.2%. SET4’s induction is constant over
five trials of the same experiment. The
results are probably not the result of chance.
It can be assumed that SET4 is induced under anaerobic conditions.
Using
the “guilt by association” method, SET4’s predicted expression pattern could be
compared with that of known genes induced under anaerobic respiration. However, this information is not available. Instead SET4’s expression pattern will be
considered during sporulation.
|
Orf |
Gene |
|
Process |
Function |
Component |
|
SET4 |
biological_process unknown |
molecular_function unknown |
not yet annotated |
||
|
|
biological_process unknown |
molecular_function unknown |
not yet annotated |
||
|
TOA2 |
transcription initiation,
from Pol II promoter |
general RNA polymerase II
transcription factor |
transcription factor TFIIA |
||
|
SRB5 |
transcription, from Pol II
promoter |
RNA polymerase II
transcription mediator |
mediator complex |
Figure 3: Microarray data for
SET4 showing expression during sporulation.
Three similar genes are shown, with a Pearson correlation of > 0.8 to
SET4. Click on a color strip to see
data for that gene. Courtesy of Expression
Connection.
SET4
appears to have similar expression patterns to two known genes, TOA2 and SRB5,
during sporulation. Their gene products
are involved in transcription. Using
the “guilt by association” method, it could be assumed that SET4 is also
involved in a related pathway. It
should be noted that this relationship is not a result of chromosome
location. SET4, TOA2, and SRB5 are on
different chromosomes.
SET4
was previously predicted not to be a transmembrane protein. Using microarray data, it can be predicted
that SET4 induces expression under anaerobic conditions and and is involved in
transcription with TOA2 and SRB5.