This web page was produced as an assignment for an undergraduate course at Davidson College
My Favorite Yeast Genes
The purpose of this page is to analyze two genes found in the Yeast genome. One of the genes is annotated meaning that much information is known about the gene. The other is non-annotated meaning that very little other than the nucleotide sequence is known. The annotated gene I chose is MCA1 and the non-annotated gene is YOR193W. I've provided as much information as I could find about each gene and for the YORCdelta21 I've tried to predict a possible function.
MCA1 - Annotated Gene
Location:
The Yeast gene MCA1 also known as YCA1 (systematic name - YOR197W) is found on Chromosome XV and is located from bp 717022-718383. Figure 1 shows where MCA1 falls on the chromosome and also names some of the genes near it (YORCdelta21, also shown in Figure 1, is the non-annotated gene analyzed on this web page).
Figure 1: This is an image of Chromosome XV. The piece of the chromosome containing the MCA1 gene blown up. Also included is the key that describes the image. Also note that the non-annotated gene I chose, YOR193W, is also shown in this image. This image taken from the SGD web site. Click on the image to find page.
Biological Process (why):
Apoptosis is cell mediated cell death. If apoptosis does not occur in organisms to control growth the effects can be detrimental. Cancer is the prime example of disease which apoptosis does not occur causing tumors to form although in many cases cancer is caused by the inability of cells to enter the G0 or inactive phase of the cell cycle. Apoptosis is characterized by condensation and subsequent fragmentation of the cell nucleus during which the plasma membrane remains intact (SGD, 2002; <http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/GO/go.pl?goid=6915>). It has been shown that the yeast genome is missing many of the gene orthologues that are thought to control apoptosis in other organisms. MCA1 is one of the only genes known to be involved in the regulation of apoptosis in yeast at this point. The protein coded by MCA1 has a similar structure to caspases, apoptosis regulators found in mammalian genomes (Madeo, et al. 2002).
Molecular Function (what):
It is thought that the MCA1 acts in much the same way as caspases found in mammalian species. The main mechanism given for apoptosis is mitochondrial dysfunction (Szallies, et al. 2002). Generally, apoptosis is the result of a breakdown of the cell nucleus while the plasma membrane is unaffected. A study done by Szallies et al., suggests that the expression of MCA1, triggered here by TbMCA4, resulted in growth inhibition, mitochondrial dysfunction, and cell death (Szallies, et al. 2002). MCA1 interacts with WWM1 which encodes a small domain protein. Over expression of WWM1 causes cell death and is only suppressed by over expression of MCA1 (Szallies, et al. 2002). In other words, MCA1 is directly involved in the regulation of cellular proliferation.
Cellular Component (where):
Judging by the functions of the protein encoded by MCA1 the protein is most likely found in the interior of the cell possibly near mitochondria. The fact that the plasma membrane is not effected by apoptosis directly suggests this, as well as the fact that research shows mitochondrial dysfunction as a mechanism for apoptosis (Szallies, et al. 2002).
Hydrophobicity also may have something to do with the function of a protein. The purpose of a Kyte Doolittle Hydropathy Plot is to determine if the protein in question has an transmembrane domain. If the data line (green) crosses the y=1.8 horizontal line (red) the plot predicts that the protein is a transmembrane protein. The plot for MCA1 (Figure 2) suggests that it is a transmembrane protein. My prediction is that it crosses the mitochondrial protein because it has been implicated in affecting mitochondrial function.
Figure 2: This graph is the Kyte Doolittle hydropathy plot for MCA1. Click on the image to find page
See Figure 3 for some information regarding the protein encoded by MCA1.:
Figure 3: This is some basic information regarding the amino acid sequence of MCA1. Click on the image to find page.
Predator search for protein information:
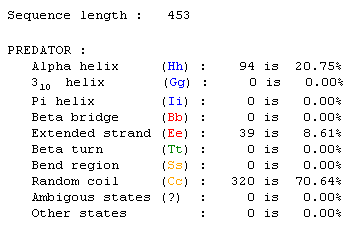
This information was obtained from a Predator search done on the protein sequence (Figure 3). The fact that the plotted line (green) crosses the axis at y=1.8 (red) suggests that this is a transmembrane protein.
Figure 3: This information was taken from a Predator search. Click on the information to find page.
Sequence Info (SGD, 2002; <http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/GO/go.pl?goid=6915>):
The nucleotide sequence is:
>YOR197W Chr 15
ATGAAGATGAGCCTCGAAGTTTATCTAAACTACCACCAAAGAAGACCGACTAGATTTACA
ATCATGTATCCAGGTAGTGGACGTTACACCTACAACAACGCTGGTGGTAATAATGGCTAC
CAACGGCCCATGGCTCCTCCACCTAACCAGCAGTATGGACAGCAATATGGTCAGCAATAT
GAACAGCAGTATGGACAGCAATATGGGCAACAAAATGATCAGCAATTCAGTCAGCAATAT
GCTCCACCACCAGGTCCTCCCCCTATGGCTTATAACAGGCCTGTGTATCCCCCCCCTCAA
TTCCAGCAGGAACAGGCAAAGGCACAATTAAGCAACGGCTACAACAATCCTAATGTAAAC
GCATCCAATATGTACGGTCCACCCCAGAATATGTCATTACCTCCACCTCAAACACAAACT
ATTCAAGGTACAGACCAACCTTATCAGTATTCTCAATGTACTGGGCGTAGAAAGGCTTTG
ATTATCGGTATAAACTACATAGGTTCAAAAAATCAACTGCGTGGTTGTATCAATGATGCT
CATAACATCTTCAACTTTTTGACTAATGGGTACGGTTACAGTTCAGATGACATTGTCATA
TTAACTGATGATCAGAACGATTTGGTCAGGGTTCCCACTAGGGCTAATATGATTAGGGCC
ATGCAATGGTTGGTCAAGGATGCGCAACCCAATGATTCTTTGTTCCTTCATTATTCTGGA
CATGGTGGCCAAACTGAAGATTTGGATGGGGACGAAGAAGATGGGATGGATGATGTTATA
TATCCGGTCGATTTCGAAACTCAAGGGCCAATTATCGACGATGAAATGCACGATATAATG
GTGAAGCCCTTACAACAAGGTGTTAGACTAACAGCATTGTTTGACTCTTGTCATTCGGGT
ACAGTGTTGGATCTTCCATATACCTATTCTACTAAGGGTATTATTAAGGAGCCCAATATT
TGGAAGGATGTTGGCCAAGATGGCCTGCAAGCAGCTATTTCATATGCCACAGGAAACAGG
GCTGCTTTGATTGGTTCTTTAGGTTCTATATTCAAGACCGTTAAGGGAGGTATGGGCAAT
AATGTGGATAGAGAACGCGTGAGACAGATCAAATTCTCAGCAGCAGATGTTGTTATGTTA
TCAGGTTCGAAGGATAATCAAACTTCTGCAGATGCTGTCGAAGATGGGCAAAATACAGGT
GCAATGTCCCACGCCTTCATCAAGGTTATGACTTTACAACCACAGCAATCATATTTATCT
CTTTTACAGAACATGAGGAAAGAATTGGCTGGTAAGTATTCTCAAAAACCACAATTATCA
TCGTCACACCCTATTGACGTAAATCTGCAATTTATTATGTAG
and the amino acid sequence is:
>YOR197W Chr 15
MKMSLEVYLNYHQRRPTRFTIMYPGSGRYTYNNAGGNNGYQRPMAPPPNQQYGQQYGQQY
EQQYGQQYGQQNDQQFSQQYAPPPGPPPMAYNRPVYPPPQFQQEQAKAQLSNGYNNPNVN
ASNMYGPPQNMSLPPPQTQTIQGTDQPYQYSQCTGRRKALIIGINYIGSKNQLRGCINDA
HNIFNFLTNGYGYSSDDIVILTDDQNDLVRVPTRANMIRAMQWLVKDAQPNDSLFLHYSG
HGGQTEDLDGDEEDGMDDVIYPVDFETQGPIIDDEMHDIMVKPLQQGVRLTALFDSCHSG
TVLDLPYTYSTKGIIKEPNIWKDVGQDGLQAAISYATGNRAALIGSLGSIFKTVKGGMGN
NVDRERVRQIKFSAADVVMLSGSKDNQTSADAVEDGQNTGAMSHAFIKVMTLQPQQSYLS
LLQNMRKELAGKYSQKPQLSSSHPIDVNLQFIM
Other searches:
-Searching the Protein Data Bank (PDB) to find a structural diagram of this protein product of MCA1 was unsuccessful.
-Searching the Gene Ontology page yielded one hit but it was of a human MCA1 gene. Interestingly, some of the terms associated with this gene were amino acid activation, cell-ell signaling, and chemotaxis.
-A blastn search was also performed (NCBI - Blast, 2002. <http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/Blast.cgi>) . It confirmed information already known about the sequence but did not provide any noteworthy additions.
YOR193W - Non-annotated Gene
Since nothing is really known about this gene sequence accept that is located near MCA1, we must rely on the sequence itself to provide information regarding the structure and function of the protein encoded by this gene.
Here is the Kyte Doolittle Hydropathy plot for the amino acid sequence:
Figure 4: This is the Kyte Doolittle Hydropathy Plot for YOR193W. The fact that the plotted line (green) crossed the horizontal axis at y=1.8 (red) suggests that the YOR193W is a transmembrane protein.
We now know that YOR193W is located close to MCA1 on chromosome 15 and that it is likely to be a transmembrane protein.
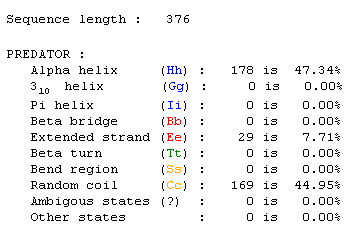
Predator search for protein information:
A search was done using Predator using the amino acid sequence for YOR193W. The results are shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5: This information was taken from a Predator search. Click on the information to find page.
See Figure 6 for information regarding the protein encoded by YOR193W:
Figure 6: This is basic information regarding the protein encoded by YOR193W. Click on the image to find page.
Sequence Info (SGD, 2002; <http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/getSeq?seq=YOR193W&flankl=0&flankr=0&map=n3map>):
The nucleotide sequence is:
ATGACATCCGATCCTGTTAATACGAATATAAGTAGCCCCACTTTAACGGACAGAAATGCA
GACGAATCATGGGAGCTCTTGAAAAGAGAGTTTAACACATTATTTAGCAACCTGAAAACT
GACAGTAAAGAAGAAGGTAATTTCACAGACAACAAAGGAGTAATCGCCAAGAAACCAATT
GTTCTGCAGGATAATGATGATTCGGATTTTACGCAGAATCAGGGAAAAGTTGCTACTGCA
ACCAGTACAACTAGTGACAGAAGCTTTAAGCGAACACTTGGTTCTATTGAAATGAAAAAA
CGTTATGTTAAGAAAAATTGCCAAGCAAAATTTGTTTTTAACACGCTTGAAGGTAAAGAA
GTTTGTTCGAAAATACTACAACATACCCTAGGCCTATTAAGTTTATTGCTATTGACGAGA
AAGATACGACTACTAAATTTTTCCTCAAAACTGCGATTGGTGATTCAACAATTGAGTTTA
TTTCGGTACTATTTGAGATTCGGAAACTTTGCGATCAATTTATATAAAATTATCAAAAGA
TTTCGCTGGTTGAGAGAAATGAAAAAACTACATTATAAAGATCAATCAATTTTATTTTAT
TTTAAAAATTTCCGGTTTTTCGACATTATTGAAGCTTTTTATAATTTGACAGATGAGTTG
ATACTGTTCCATAAGCTACAATCAATGTTTGGTAAAAAGAACACATCACATGCAAATACT
AATAGACTAATGACATTCGTCAAAGAACAGCACTATATCTTATGGGAAGTTTTAAATATT
CTTGCTATCAATAAAAACATTGAACAATGGCGACAGCTAATAAGAGATGAAATTTATTTA
AGTATCTATAATACCAGTGGTAATGCAATAAAGGAATACGAGTTAAAGTACAAACTACCT
ACCAATGACAAAGTCAATTTGGAGTTACGGAAAAATAATATTACATTGGATTTTTATAAG
ATAATACTAAACTTATTGTCTAATCTAATTAATATTAAAGGTAAAAGGGACAAATATAAC
TCAGAGCTAGCTTACGAAATAATTTCAGTAGGTTCCGGTGTTACTGAACTCCTTAAGCTA
TGGAACCGAGCCAAAGTCACTTCGGCTAATGAACATACAAGCGCTGTTTGA
The amino acid sequence is:
MTSDPVNTNISSPTLTDRNADESWELLKREFNTLFSNLKTDSKEEGNFTDNKGVIAKKPI
VLQDNDDSDFTQNQGKVATATSTTSDRSFKRTLGSIEMKKRYVKKNCQAKFVFNTLEGKE
VCSKILQHTLGLLSLLLLTRKIRLLNFSSKLRLVIQQLSLFRYYLRFGNFAINLYKIIKR
FRWLREMKKLHYKDQSILFYFKNFRFFDIIEAFYNLTDELILFHKLQSMFGKKNTSHANT
NRLMTFVKEQHYILWEVLNILAINKNIEQWRQLIRDEIYLSIYNTSGNAIKEYELKYKLP
TNDKVNLELRKNNITLDFYKIILNLLSNLINIKGKRDKYNSELAYEIISVGSGVTELLKL
WNRAKVTSANEHTSAV
Other searches:
-Searching the Protein Data Bank (PDB) to find a structural diagram of this protein product of MCA1 was unsuccessful.
-Searching the Gene Ontology page yielded no hits.
-A blastn search was also performed (NCBI - Blast, 2002. <http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/Blast.cgi>) . It confirmed information already known about the sequence but did not provide any noteworthy additions.
Predictions:
Based on the information known about YOR193W, I predict that it is a transmembrane protein that plays a role in apoptosis by affecting mitochondrial function. I make this prediction largely because it is located near MCA1.
References
Kyte Doolittle Hydropathy plot, 2002. <http://occawlonline.pearsoned.com/bookbind/pubbooks/bc_mcampbell_genomics_1/medialib/activities/kd/slrkd.pl>
Madeo, F. et al. April 2002. A caspase-related protease regulates apoptosis in yeast. Molecular Cell. 9, 4: 911-917.
NCBI - Blast, 2002. <http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/Blast.cgi>
Pole Bio-informatique Lyonnais: Predator secondary structure prediction method. 2002. <http://npsa-pbil.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=/NPSA/npsa_preda.html>
Saccharomyces Genome Database. 2002. <http://genome-www4.stanford.edu/cgi-bin/SGD/GO/go.pl?goid=6915>
Szallies, A. et al. April 24, 2002. A metacaspase of Trypanosoma brucei causes loss of respiration competence and clonal death in the yeast Sacchoromyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett. 517, 1-3: 144-150.
This page was designed by Graham Watson, a senior Biology major at Davidson College.
Click here to go back to my Home Page
© Copyright 2003 Department of Biology, Davidson College, Davidson, NC 28035
Send question to grwatson@davidson.edu