My Favorite Non-Annotated Yeast Gene: YGR058W
GENERAL INFORMATION AND LOCATION
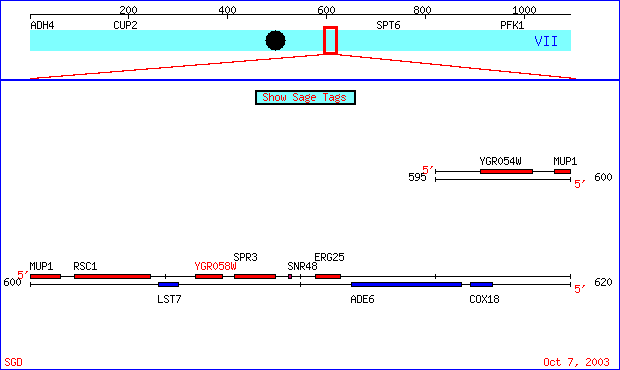
My favorite non-annotated yeast gene
is also located on chromosome 7 between bases 596137 and 617144 (as seen
on the map below provided by yeastgenome.org.
). An open reading frame in this region codes for a unknown protein
product. This 335 amino acid protein is found in several species
of yeast. The Molecular, biological, and cellular mechanisms for
this protein have not been discovered. Swiss Prot merely labels this
proteins as žhypothetical 38.4 kDa protein in MUP1-SPR3 intergenic regionÓ.
(Swiss Prot)
FIGURE 1 - This image from yeasstgenome.org shows the chromosomal location of YGR058W

Amino Acid Sequence for YGR058W:
MCAKKLKYAAGDDFVRYATPKEAMEETRREFEKEKQRQQQIKVTQAQTPNTRVHSAPIPLQTQYNKNRAE
NGHHSYGSPQSYSPRHTKTPVDPRYNVIAQKPAGRPIPPAPTHYNNLNTSAQRIASSPPPLIHNQAVPAQ
LLKKVAPASFDSREDVRDMQVATQLFHNHDVKGKNRLTAEELQNLLQNDDNSHFCISSVDALINLFGASR
FGTVNQAEFIALYKRVKSWRKVYVDNDINGSLTISVSEFHNSLQELGYLIPFEVSEKTFDQYAEFINRNG
TGKELKFDKFVEALVWLMRLTKLFRKFDTNQEGIATIQYKDFIYATLYLGRFLPH
STRUCTURE
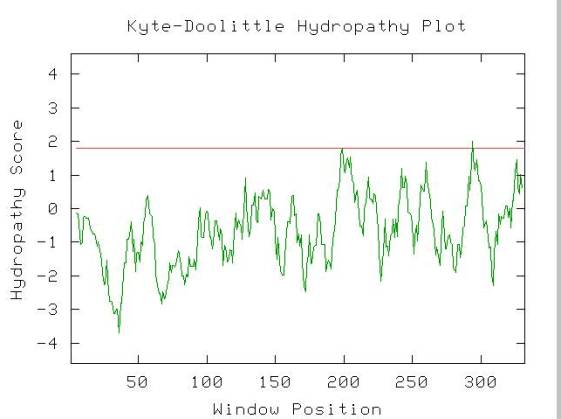
To predict the structure of this nonannotated
protein I visited the PREDATOR site. Using the amino acid sequence
I found through NCBI, PREDATOR predicted the protein's secondary structure
to contain 40% alpha helices, 51% random coils and 7.76% extended strands.
FIGURE 2 - This figure shows the
PREDATOR
predicted secondary structure of the unknown protein.

FUNCTION
To ascertain the function of this protein I searched for similar homologous proteins that could possibly reveal the biological and molecular function of this unknown protein. Using Blastp and the amino acid sequence, I searched for similar proteins within the NCBI database. Unfortunately, there were no homologous proteins found. (Blastp results) I then attempted to find any conserved domains for this unnamed protein, hoping this would reveal a possible family of proteins to which the unknown protein belongs. While there was one region conserved with another gene (called COG5126) it had a poor e-value (Conserved Domain Search). Finally, I ran the amino acid sequence on NCBI's tBlastn search. This search resulted in more promising results. The amino acid sequence had high similarity (e-127) to a gene called žSaccharomyces cerevisiae sporulation-specific septin (SPR3) geneÓ.(NCBI Nucleotide page for this gene) This 2965 base pair gene is also located on chromosome 7 and produces a 512 amino acid protein called sporulation specific septin. NCBI notes that this gene belongs to a family of bud neck microfilaments found in yeast. Thus, this gene is involved in the structural formation of budding yeast cells. From this limited information the relationship between this protein and the unknownYGR058W is difficult to determine. Yet, this finding brings this protein one step closer to characterization.
Contact: altrzebucki@davidson.edu