Starting at Square One - learning the tools
Molecular Biology Lecture Schedule for First 3 Weeks and First Exam
Readings come from Life8th Ed., by Purves et al.
Week #1 (Jan 11 - 15) (return to the begining)
| Mon. |
entrance exam, introdution, syllabus |
| Wed. |
|
| Fri. |
|
Week #2 (Jan 18 - 22) (return to the beginning)
| Mon. | Martin Luther King, Jr.
Day - Classes Cancelled |
| Wed. |
|
| Fri. |
|
Week #3 (Jan 25 - 29) (return to the beginning)
| Mon. |
|
| Wed. |
|
| Fri. |
|
Week #4 (Feb 1 - Feb 5) (return to the beginning)
| Mon. |
|
Distributed Monday Feb 1due Wednesday Feb. 3 at class time
Wed. Feb 3
Virtual Reprints
for Molecular Biology - Spring 2005
(Preliminary Readings come from Life,
by Purves et al., 8th edition)
Fri. Feb 5 and Mon. Feb. 8
Section I (How do Calcium Pumps of the SR/ER work?)
Preliminary Reading
a) Homology
b) Inhibitors
c) Calcium pump role in cell physiology
One panel from a poster describing how
immunofluorescence labeling is done.
See immunofluorescence labeling of calcium pump
in skeletal muscle.
Paper
Preliminary Reading
a) See immunofluorescence
labeling of calcium pump in non-muscle cell grown in culture.
Where is SERCA2 located in non-muscle cells?
b) Use Streptolysin-O
(SLO) to selectively permiabilize the plasma membrane.
What is SLO? What does it do? How does it work?
c) Jmol images of SERCA1a prior to and after the phosphate binding.
Paper
Preliminary Reading
a) See a cartoon showing sodium
pump subunit assemply.
How do the two sodium subunits fit together?
b) Immunopecipitation Method - Animation
Paper
Mon. Feb. 15
Papers
Wed. Feb. 17
First Web Page Due
at Class Time
optional help session on Orthologs
Fri. Feb. 19
Preliminary Reading
What is FRAP?
Optional Reading
Required Reading
Optional Reading
Required Reading
Additional Sources of Information
Section III (How do cells know to keep some proteins in the ER?)
Wed. Feb. 24 - Fri. Feb. 27
Preliminary Reading
Papers
Saturday February 27 - - Sunday March 7
Second Web Page Due March 10
Mon. March 8 - Fri. March 12
Preliminary Reading
Papers
Mon. March 15 - Wed. March 17
Amino Acid Structures for in-classs discussion
Second Exam due Monday March 22 at class time
- Optional Jmol Workshop
Section IV (Methods that Push the Envelope)
Wed. March 24
1) New Cloning Strategies
Preliminary Reading
A. Enhancer Traps
Fri. March 26
B. Yeast Two-hybrids
Monday March 29
2) Building a Better Mouse
cell-specific knockouts
Optional Reading: single-copy insertions
Wed. March 31
3) Faster Knockouts or Knockdowns
Preliminary Reading
Papers
Friday April 2
Papers
Section V (Sex determination in Mammals)
Wed. April 7
Preliminary Reading
in situ hybridization
a) cartoon of in situ hybridization
method
b) FISH Read
3 links under FISH in left frame (near bottom)
c) RT-PCR - requires
Flash Plug-in
Papers
Fri. April 9
Third Web Page Due
(no class)
Mon. April 12
Optional Reading
Wed. April 14
Preliminary Reading
SSCP
(Read points 1, 2, and 3 under the heading of "Differences
in electrophoretic mobilities of wildtype and mutant nucleic acids") -
written by John A. Wagner at School of Medical Sciences, Cornell University.
JMol tutorial of SRY binding to DNA (Note the shape of the DNA.)
Karyotyping and G-banding (click on the word "G-banding" and read the text above)
Papers
Read Abstract Only
Fri. April 16
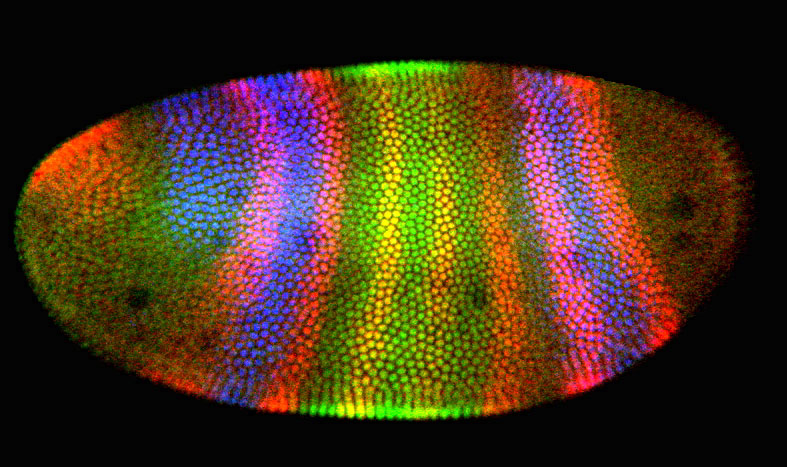
Image courtesy of Stephen W. Paddock, Eric J. Hazen, and Peter
J. DeVries (Univ. Wisconsin - Madison)
Section VI (Homeobox Genes and Their Functions)
Mon. April 19
Preliminary Reading
a) development of axis
Fly Parts
b) heat shock
c) CAT assay
Paper
Wed. April 21
Optional Reading
Fri. April 23
Preliminary Reading
Antennapedia and body parts
Read For Highlights Only
Mon. April 26
Preliminary Reading
Read For Highlights Only
Wed. April 28
Preliminary Reading
Bone formation
Papers
Final Web Page Due Friday April 30
no class meeting
Mon. May 3
Preliminary Reading
Papers
Wed. May 5
Course Evaluations