DNA Polymerase
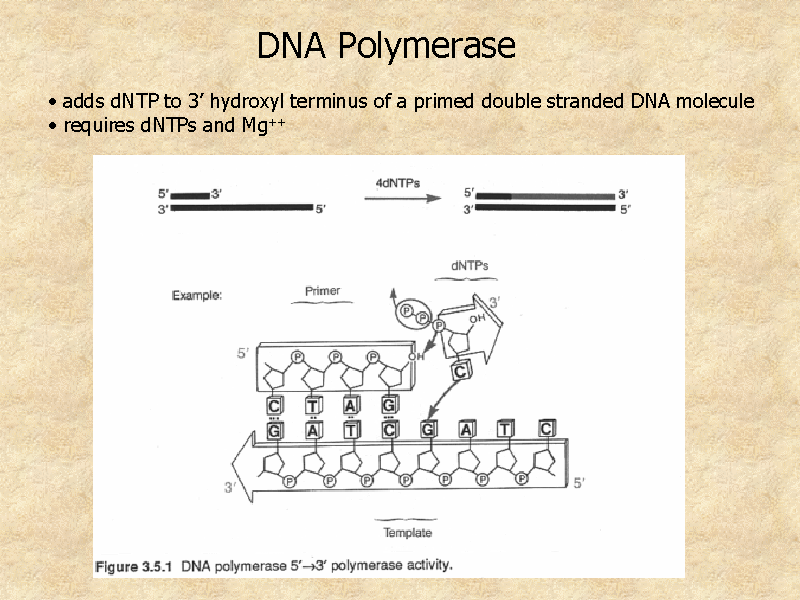
During DNA replication, DNA polymerase catalyzes the elongation of the new DNA. As replication begins at the origins of replication, new bases align with their complementary bases on the template strand. Using nucleotide triphosphates as a substrate, DNA polymerase polymerizes, or adds, the new bases to the growing 3' end of the new DNA strand.
Figure 1: DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the new DNA strand.