
This web page was produced as an assignment for an undergraduate course at Davidson College.

Triose phosphate isomerase (TIM) is a metabolic enzyme involved in glycolysis. It catalyzes the conversion of dihydroxyacetone phosphate into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
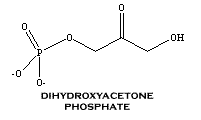

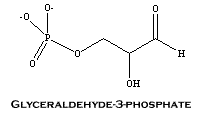
The following information was accessed through Genbank.
Chime (.pdb) image of triose phosphate isomerase (dimer):
Below are links to the amino acid and nucleotide sequences for five genome organisms:
|
Species
|
Amino Acid Sequence?
|
Nucleotide Sequence?
|
|
Yes
|
Yes, mRNA, cDNA
|
|
|
Yes
|
Yes, whole gene, cDNA
|
|
|
Yes
|
Yes, whole gene
|
|
|
Yes
|
Yes, whole gene, cDNA
|
|
|
Yes
|
Yes, whole gene
|
Go to my MacDNAsis analysis of TIM
Return to Luke's Molecular Biology Homepage
Return to Molecular Biology at Davidson College
© Copyright 2000 Department of Biology, Davidson College, Davidson, NC
28036
Send comments, questions, and suggestions to:luroberts@davidson.edu