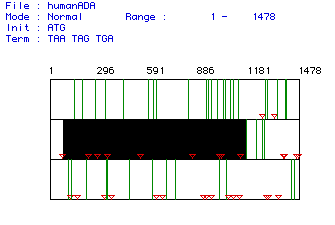

Figure 1. ORF analysis of Homo sapiens ADA mRNA. Red triangles indicate start codons, green lines indicate stop codons. Black box labels largest ORF in the mRNA sequence. ORF is nucleotides 77-1168. Click here to view the original mRNA sequence.
This ORF codes for a peptide with 364 amino acid residues and a predicted
weight of 40748.26 Daltons.
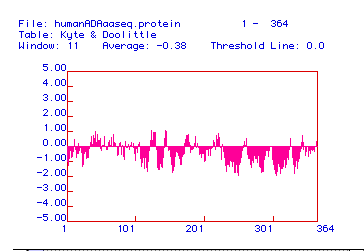
Figure 2. Ktye-Doolittle Hydrophobicity Plot for Homo sapiens
ADA. There are no points on this plot above the 2.00 threshold, so
no region of the protein is sufficiently hydrophobic to reside in a phospholipid
bilayer. Therefore, ADA is not an integral membrane protein.
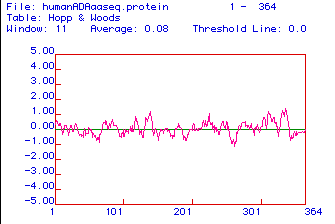
Figure 3. Hopp and Woods Hydrophilicity Plot for Homo sapiens
ADA. Highly hydrophilic domains likely suitable for use as
antibody epitopes occur near residues 130-140, 310, and 340-350.
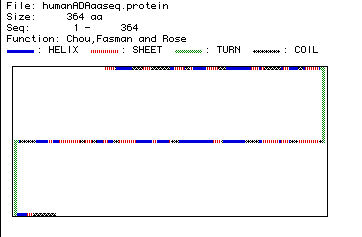
Figure 4. Secondary structure of Homo sapiens ADA as predicted
by Chou, Fasman and Rose analysis. Click here to compare this prediction
to a RasMol image of crystallized ADA.
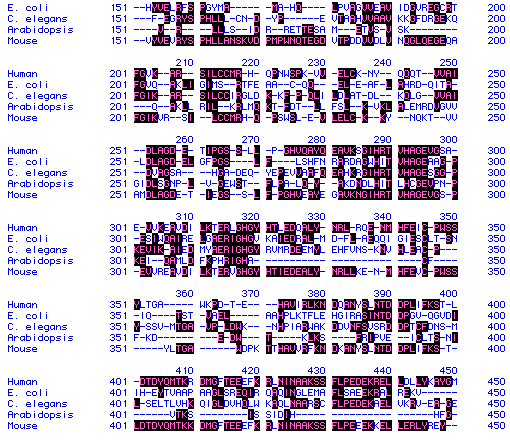
Figure 5. Sample of ADA amino acid sequence from human,
E.
coli, C. elegans, Arabidopsis,
and
mouse showing conserved residues (highlighted).
To see full amino acid sequences for each species, click on its name.
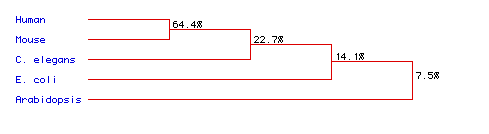
Figure 6. Phylogenetic tree for ADA from human,
mouse,
C.
elegans, E. coli, and Arabidopsis.
Phylogeny created from analysis of amino acid sequence conservation.
Numbers indicate percent conservation between species. To see full
amino acid sequences for each species, click on its name.